Why be limited by industry standards or 5G infrastructure? Share your images with anyone, anytime using sound-wave technology that transmits data at a frequency only dogs can hear.
Imagine what we could do if we could share massive volumes of data between hospital networks in a matter of milliseconds – regardless of their legal affiliation. Not only could we liberate patients’ complete medical and imaging records, making them truly portable from one healthcare facility to another, but we could also make newer services and technologies more feasible and reliable – from telemedicine visits to robot-performed telesurgery.
Two big obstacles separated this coveted fiction from becoming a reality – trust (i.e. security, privacy, and identity management) and infrastructure (i.e. server processing power and high-speed networks). There was a lot of hype surrounding blockchain for addressing the former not all that long ago, which largely fell flat because of the latter. However, the emergence of 5G networks is bringing renewed promise for enabling economies of scale in the healthcare industry that were previously unimaginable.
So what is 5G anyway, and what does it mean for healthcare?
The next-generation in mobile communication technology, 5G uses ultra-high-frequency ‘air interfaces’ that have a much higher capacity than traditional wireless networks to transmit data and bring the promise of unprecedented transmission speed and bandwidth capacity with near-zero latency.
Quite simply, this means that 5G will allow healthcare organizations to connect more devices (think IoT), send more data – both in size and volume (think growing ageing populations and hi-res CTs), and facilitate true real-time communication between care providers and patients (think robot-performed telesurgery).
This dam-breaking technology has the potential to truly support the flood of healthcare data that is being generated and continues to grow at an exponential rate. 5G is already rolling out in some major cities, and it is estimated to become mainstream by 2022 – the only problem is, healthcare won’t be able to realize the full benefit of this technology until we address the other elephant in the room – trust.
Enter the Blockchain…
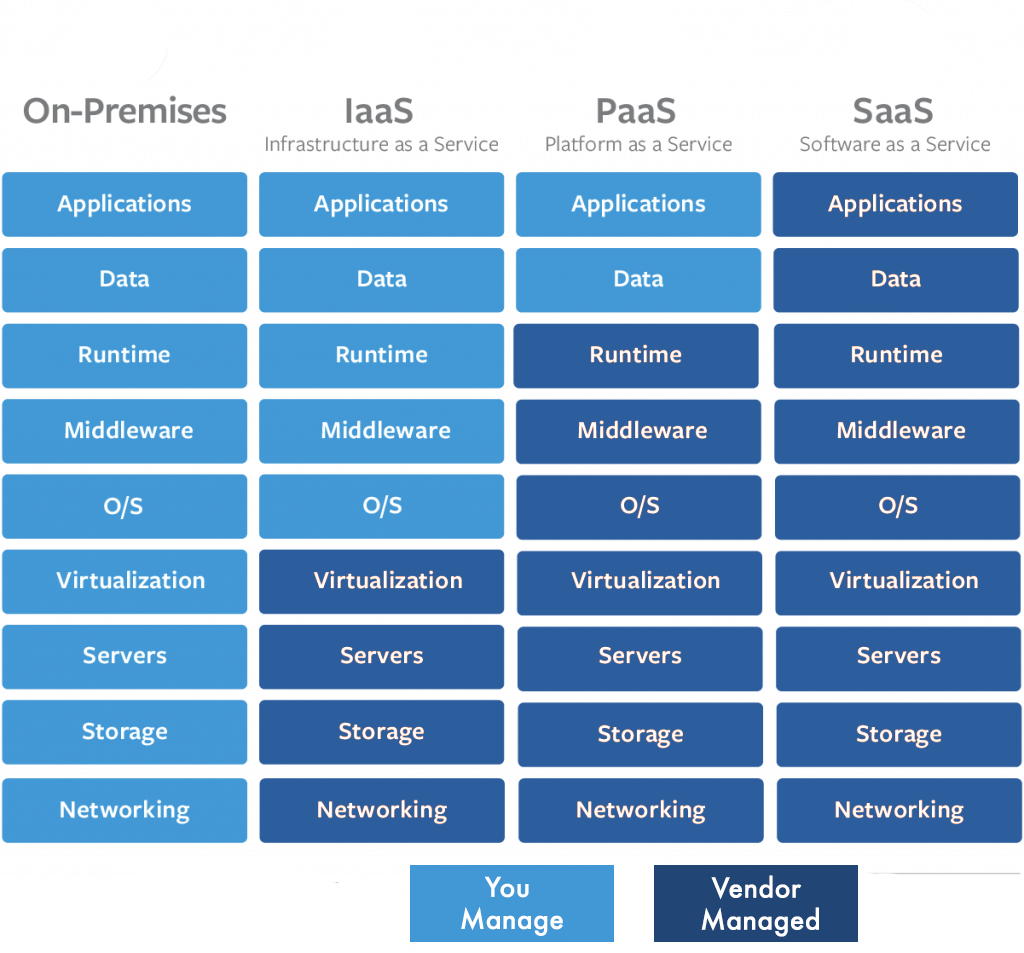
Fundamentally, Blockchain provides a secure method of indexing and sharing information across a network of unaffiliated systems. As part of a distributed and collaborative ledger each system plays an integral role in recording and validating health transactions from across the network (the existence and location of patient images, for example). All systems in a Blockchain keep a comprehensive ledger of all transactions that have occurred across the network – such as updates to an electronic health record, or the addition of a new imaging exam. When information is requested from the network consensus across participating systems is required to confirm the accuracy of data being shared. This decentralized data stewardship model ensures that information is always synchronized across the chain and prevents any one person or system from being able to corrupt or take down the network. The benefits of this model are many, but to name a few:
- Reuniting the patient record: One of the biggest interoperability challenges today is patient identity management. Because healthcare providers exist in their own technology silos patients are assigned unique identities for each facility or provider they visit – resulting in a fragmented patient record and care experience where technologies from the 90’s like CDs and fax machines are the primary method for information sharing. With Blockchain multiple patient identifiers from disparate organizations can be tracked and connected across the network, resulting in a truly unified and transparent medical record.
- Achieving real economies of scale: Most healthcare organizations would argue that their technical infrastructure is expensive, often failing to deliver the promised ROI. Because Blockchain shares resources across the network it can realize real economies of scale – leveraging compute power across the network to facilitate faster and more efficient information exchange and leveraging network-wide volume to drive down individual transaction costs.
- Facilitating faster, cheaper, and more reliable cross-entity transactions: Because a Blockchain can be shared across a variety of authorized providers in a secure and standardized way it has the potential to greatly reduce the cost and complexity of common transactions such as brokering referrals, accessing relevant medical history, communicating test results or incidental/critical findings, and managing billing and payment for network participants including but not limited to hospitals, specialists, primary care physicians, social service providers, and insurance payers, etc. And once again, because of that ledger and the inherent cryptographic protocols underlying Blockchain technology clinical and financial transactions are guaranteed to be accurate and secure.
Love the logo? Contact us for details on how to order your limited edition tee.

Are you ready for the next wave of digital transformation? We can help you separate truth from fiction and build a future-proof technology strategy that will best fit your organizational capabilities and needs. Contact us to setup a meeting at RSNA 2019.